A browser extension promoted as a privateness instrument and endorsed by main platforms quietly remodeled itself into an enormous data-collection mechanism, capturing hundreds of thousands of customers’ non-public conversations with synthetic intelligence programs and elevating new questions on belief, consent, and oversight within the booming extension economic system.
A Trusted Software, Recast in Silence
For years, City VPN Proxy occupied a cushty area of interest within the browser extension ecosystem. Marketed as a free instrument to “disguise your IP” and “defend your on-line id,” it amassed a big person base roughly six million on Google Chrome and greater than one million on Microsoft Edge together with a outstanding “Featured” badge that signaled approval from platform gatekeepers. That belief, researchers now say, proved decisive.
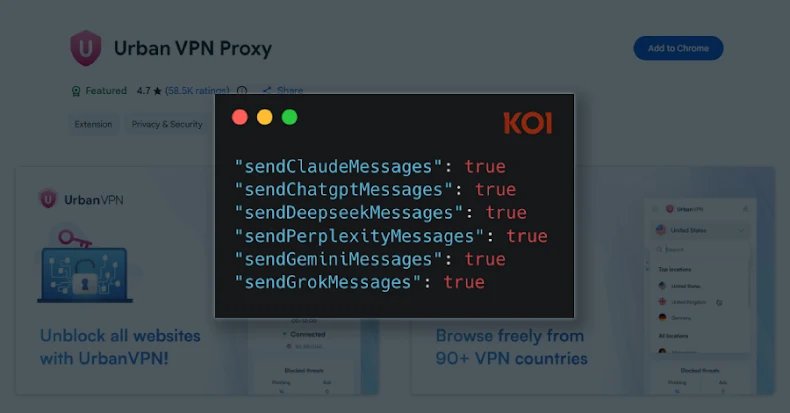
In line with findings revealed by Koi Safety, an replace pushed to customers in July 2025 basically altered the extension’s habits. With out outstanding disclosure or opt-in consent, the software program started accumulating each immediate typed into common AI chatbots together with the bots’ responses throughout companies together with OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Anthropic’s Claude, Microsoft Copilot, Google Gemini, xAI’s Grok, Meta AI, DeepSeek, and Perplexity.
Chrome and Edge extensions replace robotically by default. For customers who put in City VPN solely for its marketed digital non-public community performance, the change arrived silently, embedded in new code that redefined the extension’s objective in a single day.
How AI Conversations Had been Intercepted
Technically, the mechanism was each subtle and complete. Investigators discovered that the extension injected tailor-made JavaScript recordsdata reminiscent of chatgpt.js, claude.js, and gemini.js at any time when a person visited an AI chatbot. These scripts intercepted browser community requests by overriding customary APIs like fetch() and XMLHttpRequest(), making certain that each interplay handed via the extension first.
The outcome was an in depth file of AI use: person prompts, chatbot responses, timestamps, dialog identifiers, session metadata, and even details about which AI mannequin was getting used. That knowledge was then transmitted to distant servers managed by the developer, together with endpoints labeled analytics.urban-vpn[.]com and stats.urban-vpn[.]com.
Koi Safety recognized the identical AI-harvesting performance in three different extensions from the identical writer—1ClickVPN Proxy, City Browser Guard, and City Advert Blocker—bringing the overall set up base linked to the apply to greater than eight million customers throughout Chrome and Edge.
“AI Safety” and the Knowledge Economic system Behind It
On its public itemizing, City VPN highlighted an “AI safety” characteristic, described as a safeguard that scans prompts for private knowledge or unsafe hyperlinks and warns customers earlier than they submit them. Researchers argue that this framing obscured a extra consequential actuality: the monitoring occurred no matter whether or not the characteristic was enabled.
In apply, stated Idan Dardikman of Koi Safety, the extension warned customers about sharing delicate info with AI programs whereas concurrently exfiltrating those self same conversations to its personal infrastructure. One recipient of that knowledge, in response to the corporate’s disclosures, was an affiliated promoting and brand-intelligence agency referred to as BIScience, which makes use of uncooked, non-anonymized searching knowledge to generate insights “commercially used and shared with enterprise companions.”
BIScience, which additionally owns City Cyber Safety Inc., has confronted earlier scrutiny from researchers over alleged assortment of searching histories below what had been described as deceptive privateness coverage disclosures. Investigators say the corporate supplied software program improvement kits to third-party builders, permitting clickstream knowledge to be transmitted to domains below its management.
City VPN’s up to date privateness coverage, dated June 25, 2025, states that AI immediate knowledge could also be collected to boost protected searching and for advertising analytics, with secondary makes use of performed on de-identified or aggregated info. Researchers counter that technical proof reveals delicate content material being captured in full earlier than any such filtering.
Badges, Blind Spots, and Platform Belief
Maybe probably the most unsettling side of the episode is how seamlessly the information assortment scaled. Aside from one Edge itemizing, the extensions carried “Featured” badges—alerts that, for a lot of customers, suggest heightened evaluation and high quality requirements.
“These badges are the distinction between putting in an extension and passing it by,” Dardikman famous. “They operate as an implicit endorsement.”
The case highlights a broader vulnerability in browser marketplaces, the place insurance policies enable entry to searching knowledge below narrowly outlined “authorised use circumstances.” By tying knowledge assortment to user-facing options like AI security or advert blocking, builders can declare that broad permissions are mandatory to enhance a single acknowledged objective.

Leave a Reply