-
The Financial institution of England’s Monetary Coverage Committee (FPC) diminished its benchmark capital requirement for UK banks from %14 to %13 of risk-weighted property (RWAs).
-
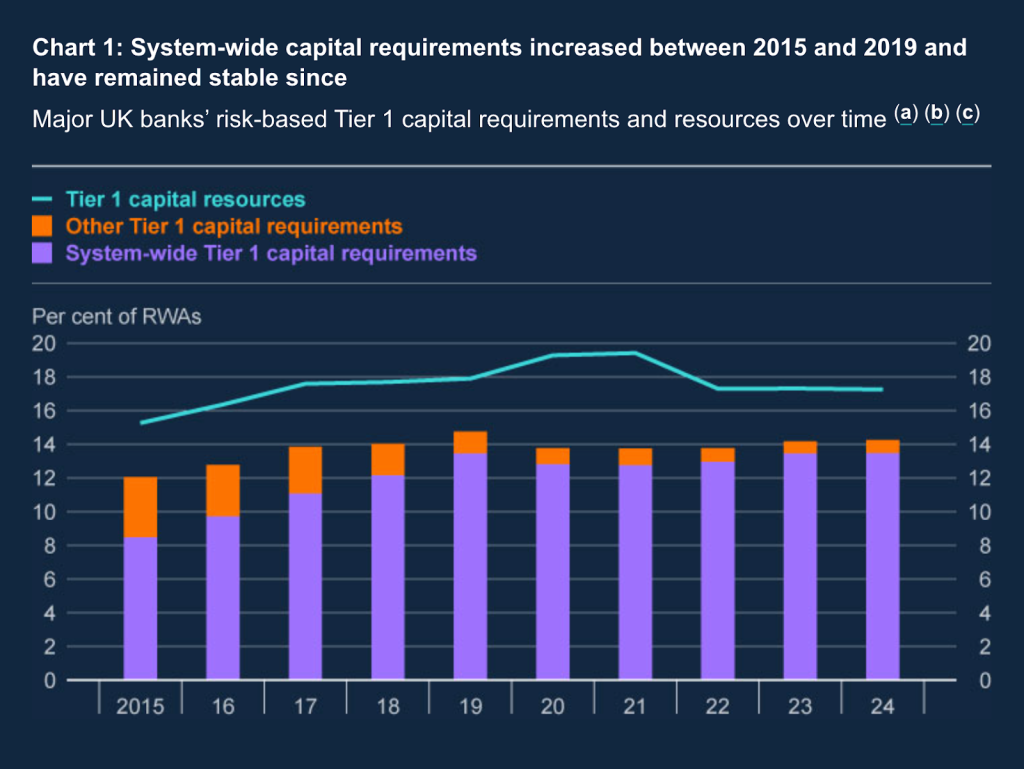
Following a decline in common danger weights since 2016, a rising variety of main UK banks are actually extra constrained by leverage ratio necessities than by risk-weighted measures.
-
The FPC plans to assessment the implementation of the leverage ratio, significantly specializing in regulatory buffers, which is important since UK necessities for giant home banks at the moment exceed these within the eurozone and the US.
The Financial institution of England’s Monetary Coverage Committee (FPC) has diminished its benchmark capital requirement for UK banks to 13% of risk-weighted property, down from 14%, a transfer that might present modest aid to commerce finance operations which have confronted mounting strain from regulatory constraints. This comes shortly after the UK Price range, throughout which Chancellor of the Exchequer Rachel Reeves urged the BoE to implement measures to jumpstart the UK economic system.
The discount, introduced within the FPC’s newest Monetary Stability in Focus paper, comes as commerce finance suppliers have more and more discovered themselves constrained by leverage ratio necessities reasonably than risk-weighted capital guidelines – a shift with explicit implications for the low-margin, high-volume enterprise of letters of credit score and provide chain financing.
The issue is acute for domestically-focused banks that keep substantial commerce finance operations. Three of seven main UK banks now discover leverage necessities extra binding than risk-weighted measures, following a 7.5 share level decline in common danger weights since 2016. This has successfully tightened the constraint on stability sheet enlargement, even because the nominal danger related to commerce exposures has remained steady or declined.
For commerce finance desks, the problem lies within the economics of the enterprise mannequin. Documentary credit and comparable devices usually carry low danger weights – typically reflecting robust collateralisation by means of underlying items and established mitigation practices. But these identical devices devour leverage capability on the identical price as higher-risk exposures, making them much less engaging when leverage turns into the binding constraint.
The FPC’s determination to assessment leverage ratio implementation, with explicit concentrate on regulatory buffers, may show important. UK leverage necessities for giant domestically-focused banks at the moment exceed these within the eurozone and the US, partly reflecting the FPC’s determination to use systemic buffers throughout each risk-weighted and leverage frameworks.
The committee’s benchmark discount ought to translate to roughly £60 billion much less nominal capital required throughout the system, primarily based on present stability sheet sizes.
Extra promising is the FPC’s dedication to enhancing buffer usability; proof from the COVID-19 interval revealed banks’ reluctance to make use of non-releasable buffers, even when regulators explicitly inspired it.
The Financial institution’s meant assessment of how totally different home publicity necessities work together – together with the countercyclical buffer, systemically essential establishment buffers, and Pillar 2A necessities for geographic credit score focus – may deal with longstanding business considerations about overlapping constraints on UK-focused lending.
UK banks at the moment keep roughly £37 billion in mixture capital headroom above their necessities, suggesting room to broaden lending, together with commerce finance, with out fast capital raises. Nonetheless, the binding nature of leverage necessities for a number of main gamers means this headroom might not translate readily into elevated commerce capability.
The implementation of Basel 3.1 in January 2027 ought to deliver additional aid, with Pillar 2A necessities anticipated to fall by roughly half a share level as danger measurement improves. For commerce finance, with its usually sturdy collateralisation and danger mitigation, this might show useful if it reduces the calibration of focus danger add-ons.
The FPC’s revised framework represents cautious easing reasonably than dramatic liberalisation, however for commerce finance suppliers working on skinny margins, even incremental aid may assist continued provision of significant providers to UK exporters and importers.

Leave a Reply